QR Demodulation in MIMO Systems
Efficient QR Decomposition for MIMO Signal Demodulation
Overview
The project focuses on implementing a QR Decomposition (QRD) module, a critical component in modern wireless communication systems, for a 4x4 MIMO receiver. By transforming complex channel matrices into simpler forms, QRD enables efficient Maximum Likelihood (ML) demodulation, enhancing system reliability and throughput in the presence of AWGN (Additive White Gaussian Noise).
The implementation is based on the Modified Gram-Schmidt algorithm, which decomposes the channel matrix (H) into:
- Q: An orthogonal matrix
- R: An upper triangular matrix
This approach reduces computational complexity and optimizes signal recovery.
Algorithm: Modified Gram-Schmidt
The QR Decomposition process involves:
- Vector Normalization: Calculating Euclidean distances to normalize channel vectors.
- Iterative Updates: Using the Gram-Schmidt process to orthogonalize and update signal vectors.
- Matrix Generation: Producing the orthogonal matrix (Q) and upper triangular matrix (R) for efficient decoding.
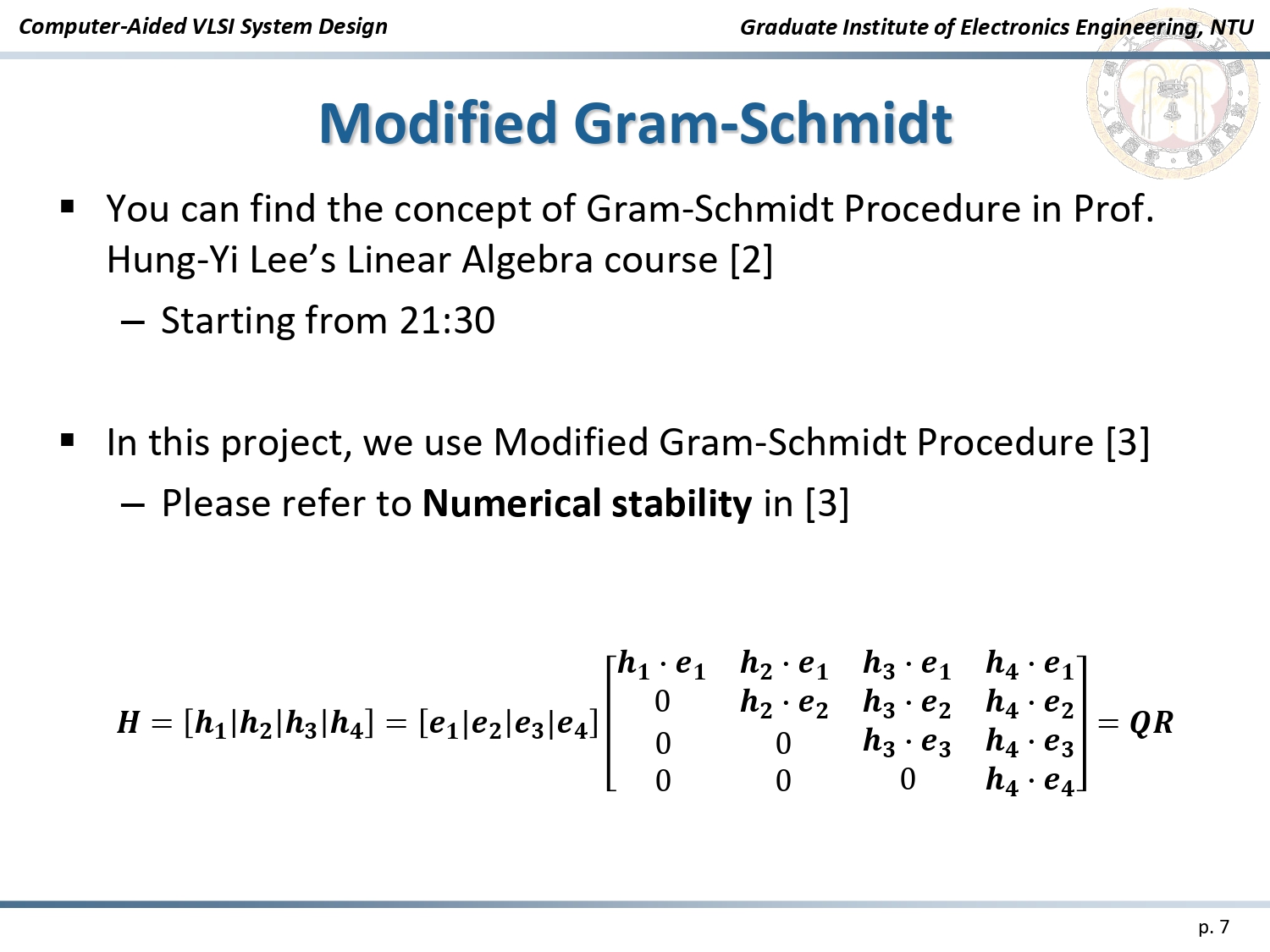
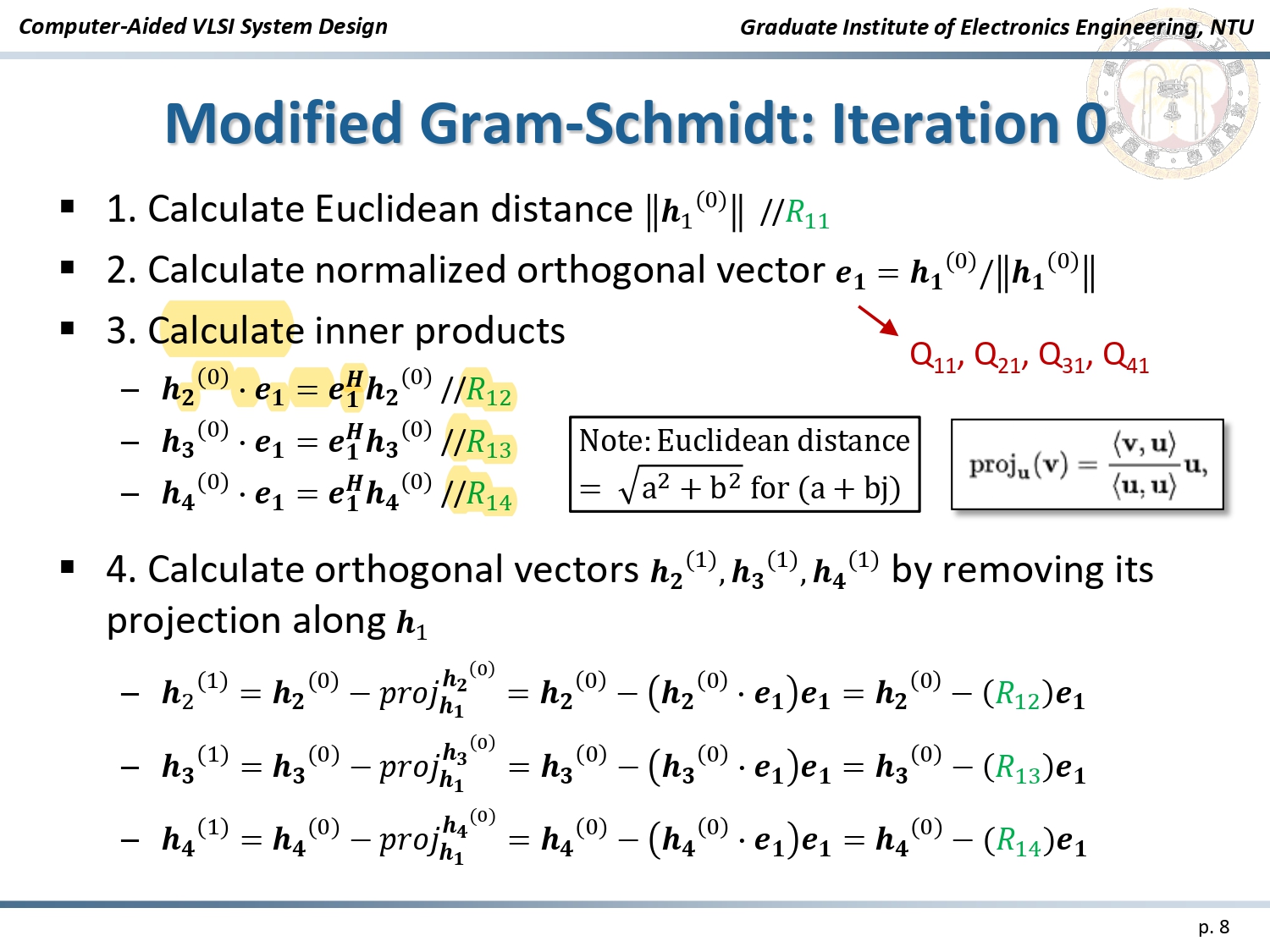
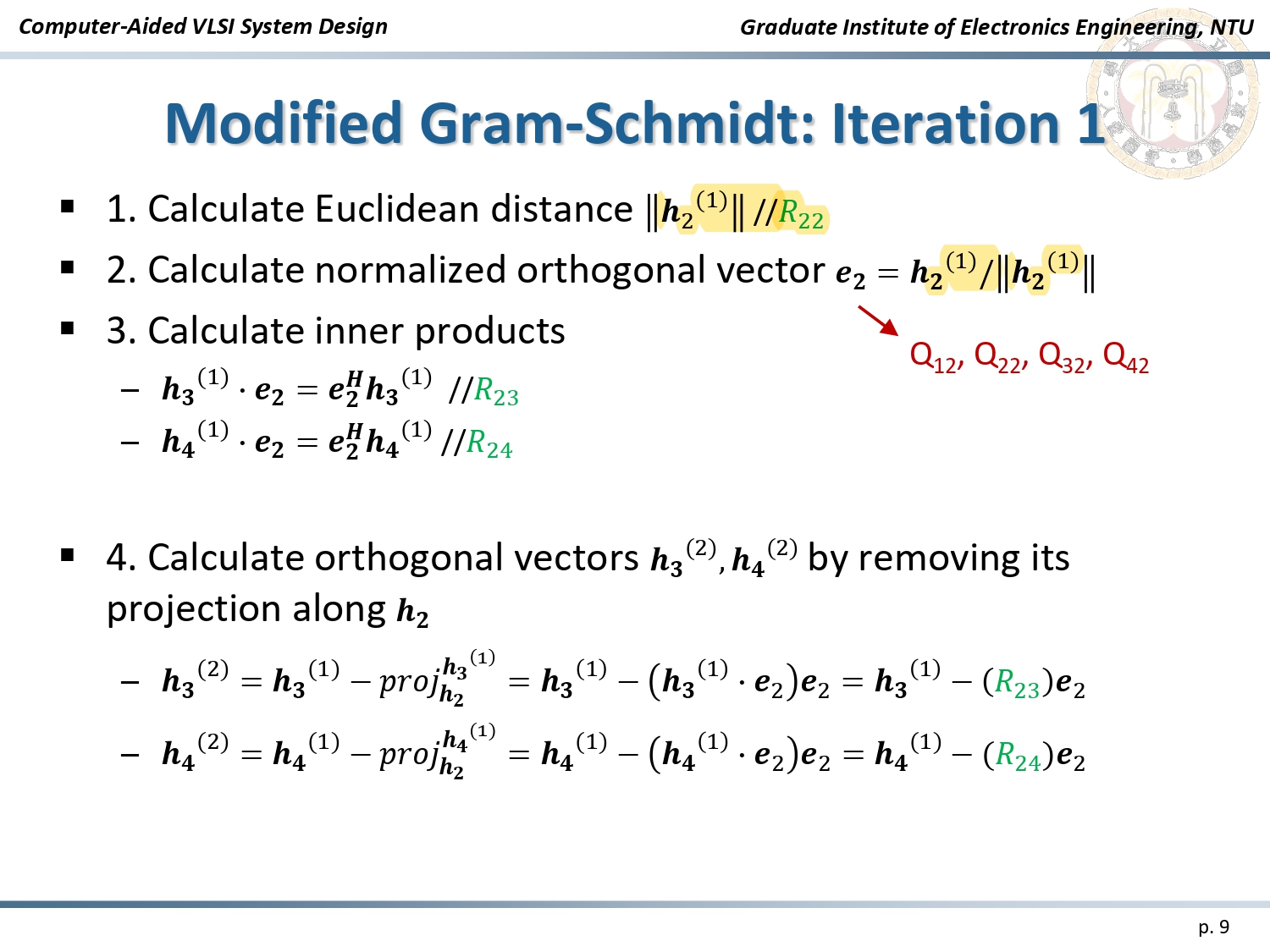
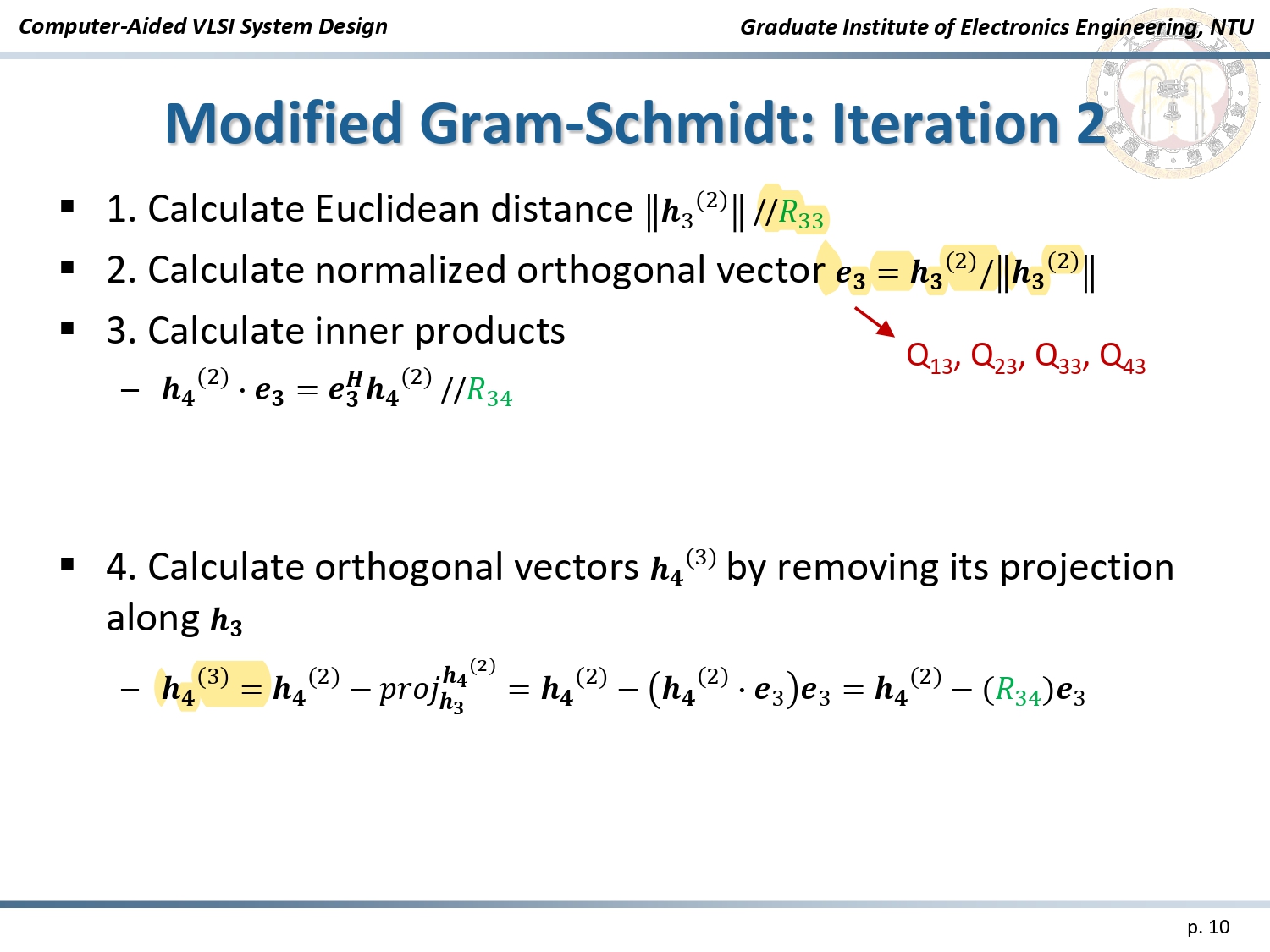
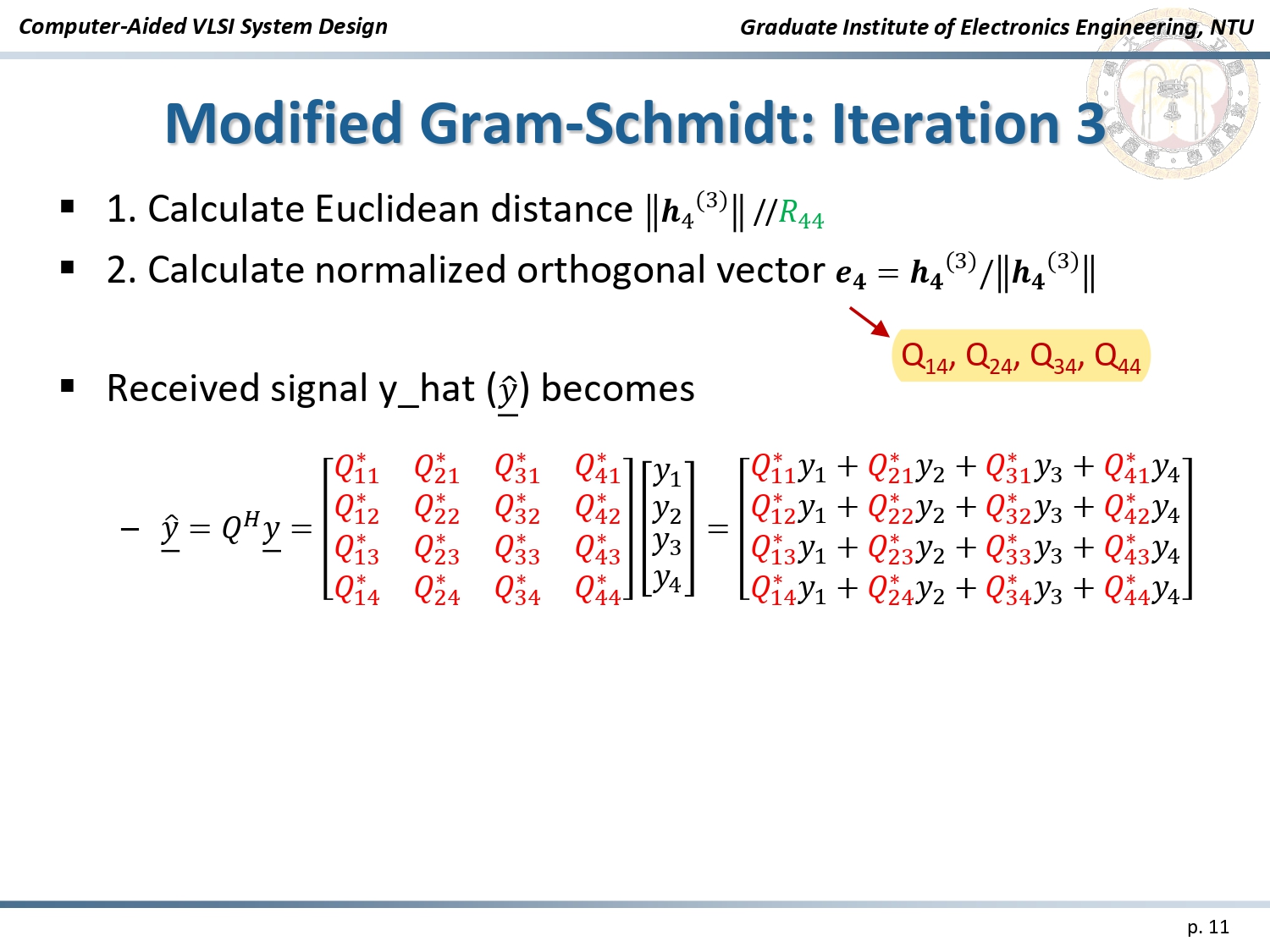
Iteration Process of Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm
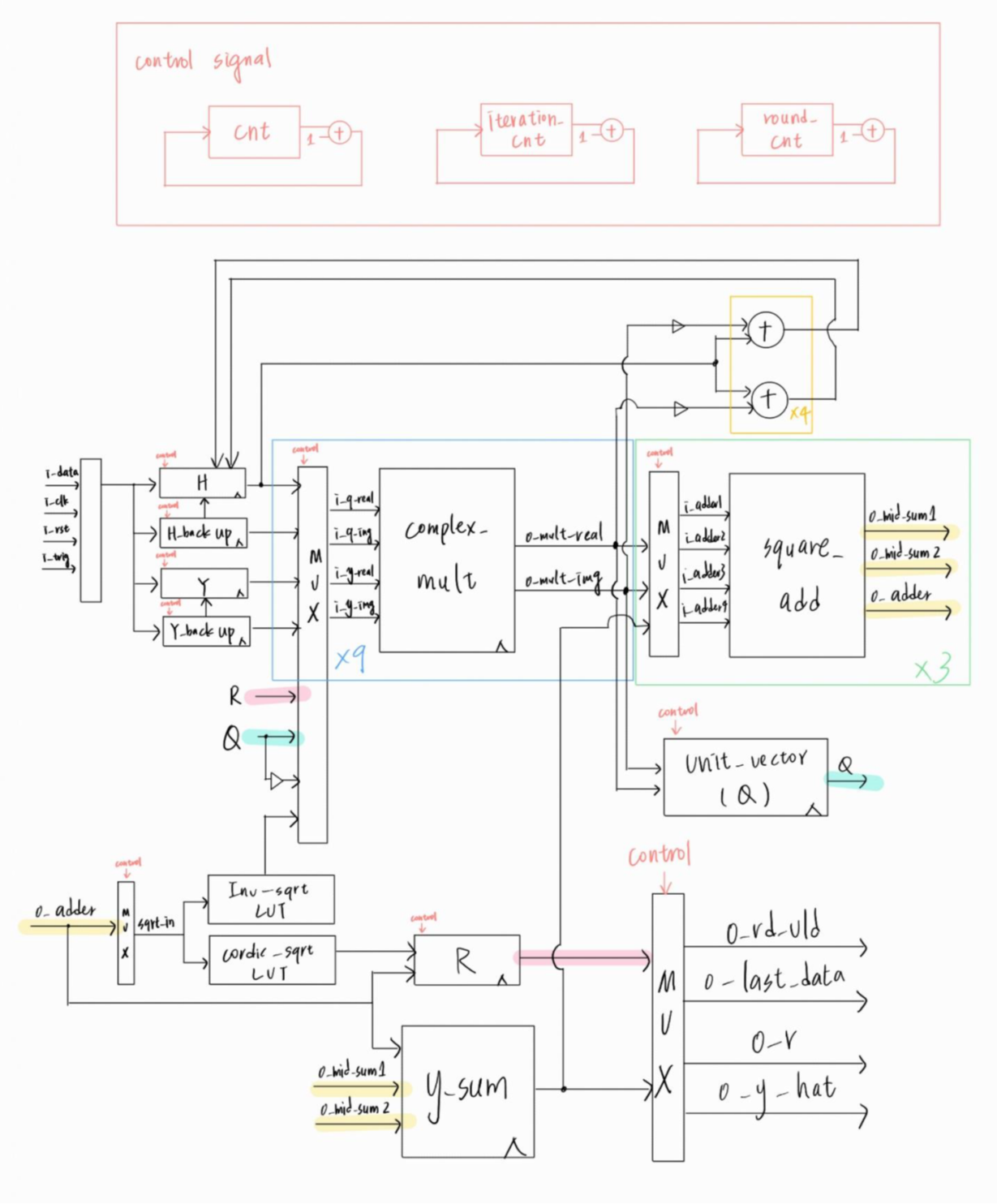
Methodology
- Fixed-Point Configuration
- Register Design: Optimized register bit-widths to balance precision and hardware efficiency.
- LUTs for Arithmetic Operations: Leveraged Look-Up Tables (LUTs) for fast square and square root calculations, reducing computational delay.
- Pipelined Architecture
- Stage Division: The computation process was divided into multiple stages, enabling parallel operations and minimizing latency.
- Resource Sharing: Efficiently shared resources across pipeline stages to improve utilization.
- Throughput Optimization: Achieved high processing speeds with minimal resource overhead.

We precisely arrange each processing unit (i.e. Multiplier, Adder and other) usage to ensure maximum usage in every cycle.
Block Diagram
Results
Post-Layout Performance Ranked 3rd in All Undergraduate Teams
- Area: 827604.71 um^2
- Latency: 100161.5 ns
- Power: 46.8 mW